
Decisions related to fixing prices are usually taken in the course of developing new products, embarking on market development, or bidding for contracts. To create value for a product the marketing department or the product line manager may decide on the best way to fixed price after taken into consideration these variables:
• Selecting a Pricing Objective: The first issue a business should consider before fixing its price is the objective of setting a price. Such objective may be spelled out when a business wants to survive against challenges like; overcapacity, intense competition or changing consumers’ taste. By estimating demands and costs associated to alternative prices a business may decide to fixed price with an aim of; maximizing it’s market share, maximized its profitability, generate positive cash flow, and a high rate of return on investment. A business may also set its price objective with an aim of becoming a product-quality leader so that its product can be perceived as luxurious or qualitative product.

• Demand: The demand for new products as well as existing ones will determine how and why prices are fixed. Demand as relates to pricing comes to mind by taking into consideration; the aggregate demand, buyer price acceptance, and price elasticity of demand.
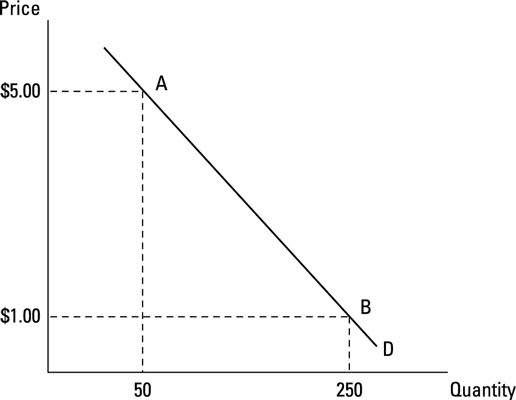
The aggregate demand indicates the total number of individual buyers who might be willing to accept the price for a product. To make a price acceptable, a business needs to find out at what price the buyers are willing to pay and then work things out to see if raw materials, labour cost, and any other cost will permit a profitable production.
To fixed price a business needs to know how demand for its product would respond towards a change in price as; price elasticity of demand may depends on the magnitude and direction of the contemplated price change.
Apart from above identified demand factors a business may also needs to measure its demand curve by adopting either of these methods: ✓Survey: Exploring the number of units consumers will buy at propose price.
✓Price experiment: Charging different prices for the same product in similar territories to see how it may affect sales.
✓Statistical analysis: Obtaining past prices, quantities sold, and other factors to reveal their relationships.
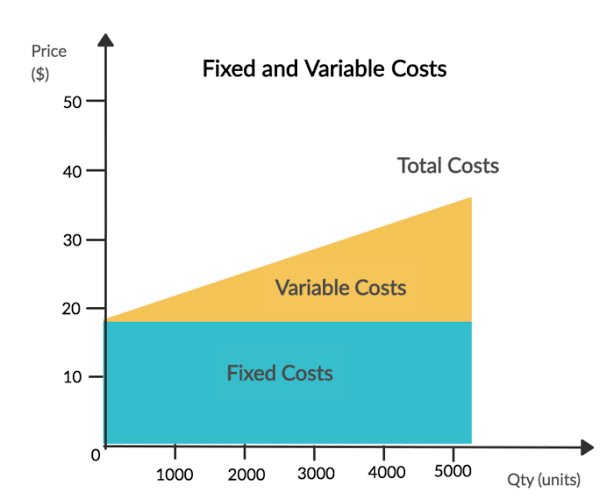
• Estimating cost: Production cost set the level at which price of goods and services should not fall below. In a situation where a product’s price is lower than its cost of production, the volume of products produced may be on the high side. In relating costs to price there is need for costs to be classify either as fixed or variable costs. Fixed costs are costs which do not vary with the level of Production. Variable costs are costs which relates with the level production.
To fixed price, a business needs to charge price that will cover the total cost of Production and know how such cost may vary with different levels of Production; as failure to measure cost correctly may lead to misallocating marketing efforts, thus not measuring profitability correctly.
• Competition: A competitor is any business which provides satisfaction to other business customer’s needs. Fixing a lower price can be interpreted by competitors as intension of a business to steal their market or wants the industry to reduce price to stimulate total demand. To fixed price above competition may require additional features to a product. The price of products can also be matched against competitors’ prices with the product features remain unchanged but focus will shift to product quality.
Information as regards to competition can be obtain by seeking opinions from existing customers as partains to competitors and their plans. The internet, print media, suppliers may also provide information about competition as competitors’ ads may revealed their intentions regarding their markets and products.

• Selecting a Pricing Method: In fixing price there is need to adopt a pricing method. By Taking decision as regards to a recommended pricing method there is need to take into consideration the; floor price, competitor’s price, and ceiling price.
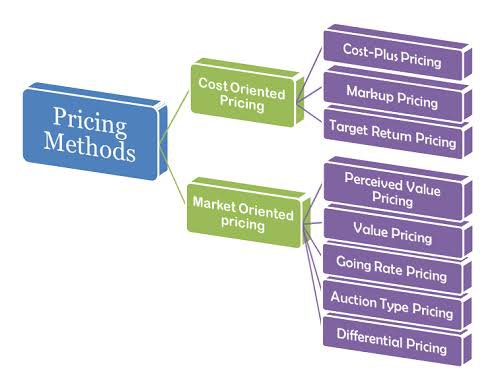
A business may also need to select a price method after examining either of the following pricing methods:
✓ Markup pricing: Markup pricing involves adding together the cost of products and certain percentage as mark-up to determine the selling price.
✓Target-return pricing: Target-return pricing is determine by considering the amount invested in business activities and the return expected from the quantity of goods to be sold.
✓ Perceived-value pricing: Adopting Perceived-value pricing will entails the price of a product will be set base on the product image a customer carries in mind and how much he is willing to pay for.
✓Value pricing: Value pricing is a customer-focused pricing model in which a business will based its price on how much the customer believes a product is worth.
✓Going-rate pricing: Going-rate pricing is adopted base on competitors’ prices. Going-rate pricing is quite popular in situations where; competitive response is uncertain or the going price will reflect the industry’s collective wisdom.
✓Auction-type pricing: Auction-type pricing is adopted when a product is offered for bids, bids taken, and afterwards sold to the highest bidder. The auction-type pricing is growing more popular especially with the growth of internet.
✓Differential pricing: Differential pricing involves charging different prices for the same type of product to different customers based on product form, payment terms, purchase and delivery time, and customer segment.

CONCLUSION
To make a product attractive and create value on the mind of a customer it is imperative for a business to look into the identified factors before setting a price. Taking decision on the best pricing option may requires a business to also look into its pricing policies and structure. It is however necessary to set a price tag that will reflects the value the customers are willing to pay.